What Does Causation Mean In Tort Law
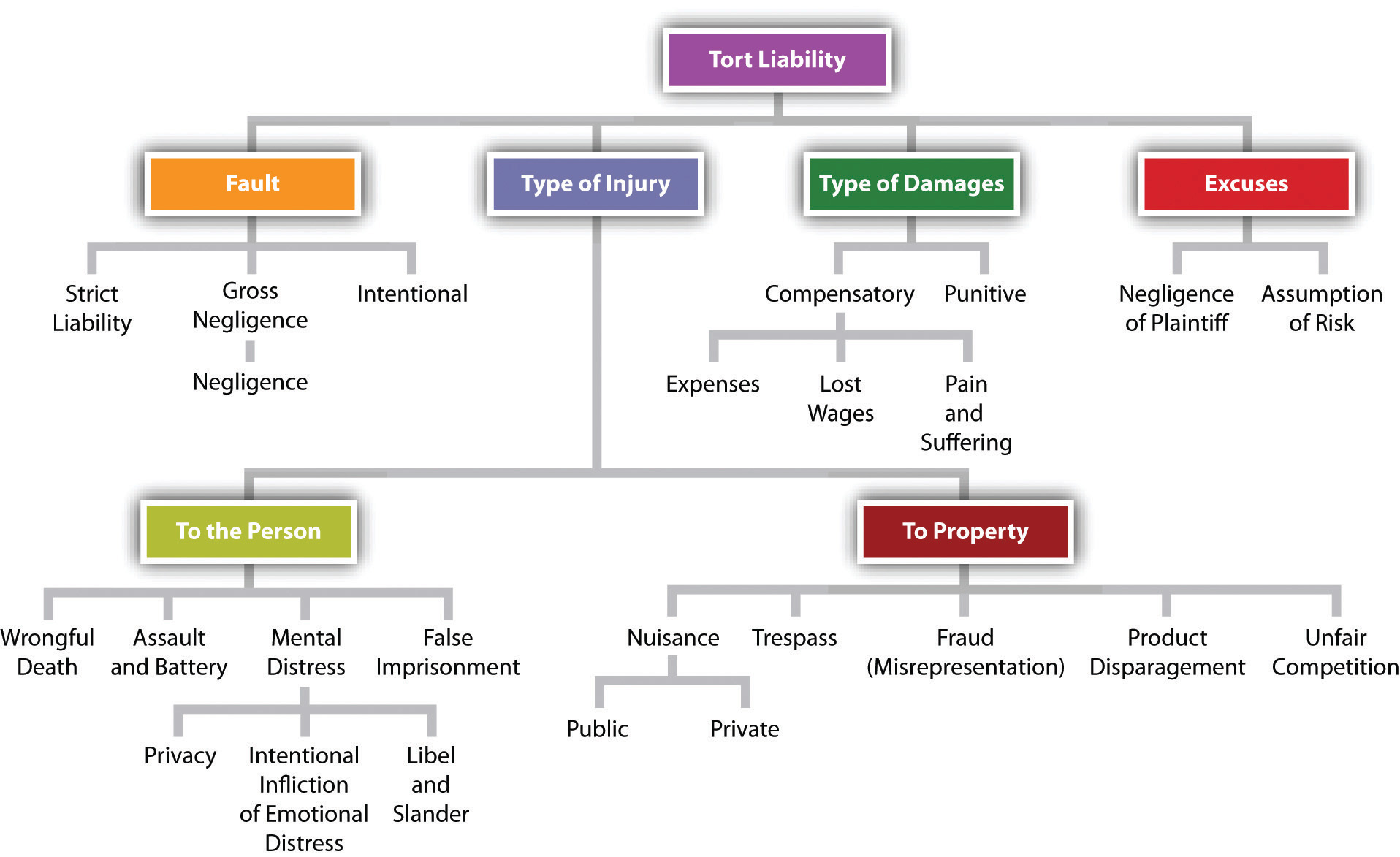
That is because of 3 the concept of causation. A defendant commits simple battery only if she intentionally causes bodily contact with another.
 What Is The Legal Definition Of Causation Wkw
What Is The Legal Definition Of Causation Wkw
In a personal injury case one must establish causationmeaning that its not enough to show that the defendant was negligent.
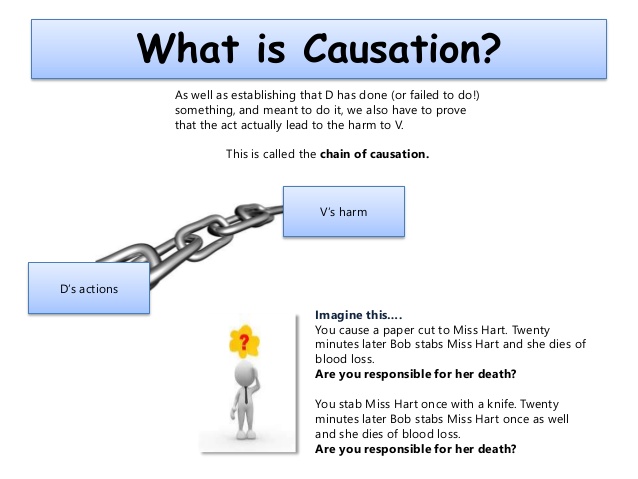
What does causation mean in tort law. There are actually two aspects of cause which are known as cause in fact and proximate or legal cause. It is the act or process that produces an effect. The defendants conduct was a cause of the plaintiffs harm if the harm would not have occurred absent the defendants negligence ie without which the harm would not have occurred.
The first requirement is that of cause in fact. It means that but for the negligent act or omission of the defendant the plaintiff would not have been harmed. A plaintiff in a tort action should prove a duty to do or not do an action and a breach of that duty.
First a tort must be the cause in fact of a particular injury which means that a specific act must actually have resulted in injury to another. Factual Causation Is Essential to Tort Liability Academicians who seek an overarching theoretical justification of tort law fall into two main camps4 Economic analysts assert that tort law should and by and large does aim at promoting efficient resource allocation5 Corrective-justice6 theorists hold that tort. Causation is the causal relationship between the defendants conduct and end result.
This is known as the but for test. The concept of causation is central to myriad areas of tort law. Causation is the relationship of cause and effect of an act or omission and damages alleged in a tort or personal injury action.
A plaintiff in a tort action should prove a duty to do or not do an action and a breach of that duty. The Laws Explicit Definition of Causation 21 The dominant two-tier definition of causation in the law. The traditional legal model of but-for causation necessary condition causation while fundamental to the idea of causation in general is insufficient to account for causation in overdetermined causation cases.
Actual cause is sometimes referred to as cause in fact. 13 An action is not. Think of this as establishing a cause and effect relationship between the defendants actions and the injuries of the plaintiff.
In other words the question asked is but for the defendants actions would the harm have occurred. Causation means the causing or producing of an event. Cause in fact simply means that the accident would not have occurred except for the fact of the defendants negligence.
Causation means the causing or producing of an event. Proximate cause is the primary cause of the injury but it does not mean that it is the only cause or even the closest cause to the accident. Tort law or the area of law in which someone suffers harm and results in legal liability can become extremely complicated once you get into the nuts and bolts.
Causation in legal terms refers to the relationship of cause and effect between one event or action and the result. Causation only applies where a result has been achieved and therefore is immaterial with regard to inchoate offenses. In criminal law it is defined as the actus reus from which the specific injury or other effect arose and is combined with mens rea to comprise the elements of guilt.
At its root causation means that the actions of the defendant led to the plaintiffs injuries. In other words causation provides a means of connecting conduct with a resulting effect typically an injury. The conventional wisdom about the causation requirement in both criminal law and torts is that it in reality consists of two very different requirements for liability.
There are two types of negligent causation actual cause and proximate cause. Factual Causation Much like the criminal law tort law uses a but for test in order to establish a factual link between the conduct of the defendant and the injuries of the claimant. Causation is an element common to all three branches of torts.
Shouse Law Group Personal Injury Negligence Proximate Causation. The third element of negligence is causation. In tort or personal injury law proximate causation refers to an act or omission significant enough in the chain of events leading to an injury that the law holds the person liable to the victim s.
Strict liability negligence and intentional wrongs. The issue of cause or causation is not as simple as it may seem. Accordingly once factual causation is established it is necessary to ask whether the law is prepared to attribute the damage to the particular breach notwithstanding the factual connection.
Legal causation is different from factual causation which raises the question whether the damage resulted from the breach of contract or duty. Causation Law and Legal Definition. Meaning ofcausal connection the way to test whether it exists in a given case is to ask whether in the circumstances the hannful result would have occurred in the absence ofthe wrongful act.
Causation is the relationship of cause and effect of an act or omission and damages alleged in a tort or personal injury action. Causation has two prongs.
 Tort Law Part 6 The Lawyers Jurists
Tort Law Part 6 The Lawyers Jurists
 Tort Law Part 5 The Lawyers Jurists
Tort Law Part 5 The Lawyers Jurists
 Pdf Factual Causation And Scope Of Liability What S The Difference
Pdf Factual Causation And Scope Of Liability What S The Difference
 What Is Tort Law Definition System Examples
What Is Tort Law Definition System Examples
 Tort Law Causation Essay Tort Law Studocu
Tort Law Causation Essay Tort Law Studocu
 Causation And Legal Responsibility In Negligence Cases
Causation And Legal Responsibility In Negligence Cases
 Pdf Causation And The Goals Of Tort Law Donal Nolan Academia Edu
Pdf Causation And The Goals Of Tort Law Donal Nolan Academia Edu
 L 7 L 8 Factual And Legal Causation Studocu
L 7 L 8 Factual And Legal Causation Studocu
 Pdf Causation Contribution And Clements Revisiting The Material Contribution Test In Canadian Tort Law
Pdf Causation Contribution And Clements Revisiting The Material Contribution Test In Canadian Tort Law
 Solved Chapter 2 Tort Law Match Each Term With Its Cor Chegg Com
Solved Chapter 2 Tort Law Match Each Term With Its Cor Chegg Com
 More Grief On Uncertain Causation In Tort The Cambridge Law Journal Cambridge Core
More Grief On Uncertain Causation In Tort The Cambridge Law Journal Cambridge Core
 Negligence Under Florida Law Gulisano Law Pllc
Negligence Under Florida Law Gulisano Law Pllc
Https Eprints Utas Edu Au 9106 2 Coady Pdf